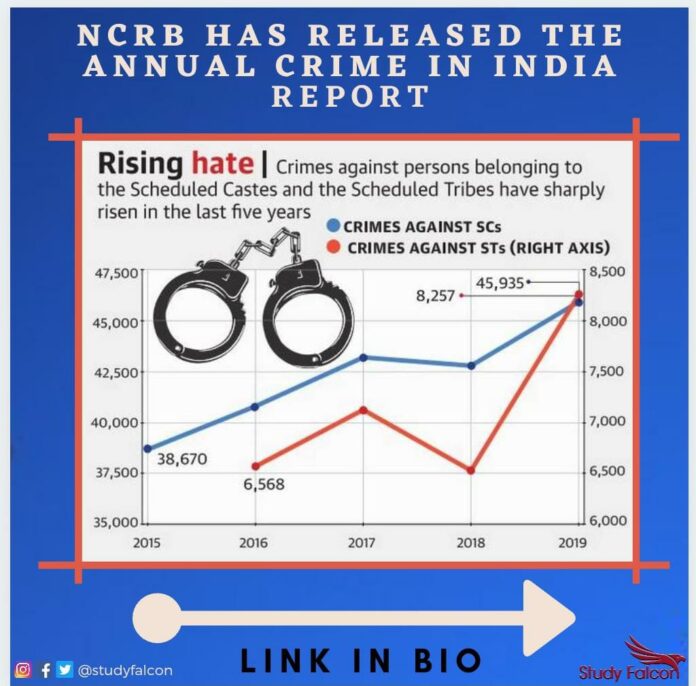
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released the annual Crime in India 2019 report. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) has released the annual Crime in India 2019 report. It reports an increase in crimes against Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) in the year 2019 as compared to the year 2018.
Crimes against SCs and STs:
Crime against SCs have increased by over 7% and crimes against STs have increased by 26% in year 2019 compared to 2018.Uttar Pradesh recorded
the highest number of crimes against SCs in 2019, followed by
Rajasthan and Bihar. Madhya
Pradesh recorded the highest
number of cases against STs, followed by
Rajasthan, and Odisha.
Crimes against SCs and STs include the atrocities committed by non-SC/ST members under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities Act), 1989 (POA Act) Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955 : It prescribes punishment for the preaching and practice of Untouchability.
Lack of Data
According to the Commonwealth
Human Rights Initiative (CHRI), very few cases were being registered for
specific discriminatory action against SCs and STs under the POA Act.Such
actions are registered mainly when accompanied by any of the
IPC offences liek rape, murders etc.
Also, there is no data on total complaints received on crimes against the Scheduled Castes, the only data available is the number of cases registered.

Cognizable Crimes:
An increase of 1.6% in
registration of cognizable crimes in 2019 as compared to 2018 was recorded.
Cognizable crimes comprise Indian
Penal Code (IPC) ones and Special and Local Laws (SLL) crimes.
Cognisable offence
means an offence in which a police officer has the authority to make an arrest
without a warrant. SLL are Acts that are framed by the state government for
specific issues
Crimes Against Women:
Crime against
women showed an increase of 7.3% in 2019 from 2018.
88 cases of crimes
against women were recorded per day. Majority of cases under crime against
women under IPC were registered under cruelty
by husband or his relatives (30.9%), followed
by assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty, kidnapping & abduction
of women and rape . In the number of cases of rape of women belonging to SCs, Rajasthan topped the list, followed by Uttar Pradesh and Madhya
Pradesh.
Cybercrimes have Increased by 63.5% in 2019. 60.4% of cybercrime cases registered were for the motive of fraud followed by sexual exploitation.
The Supreme Court
recently upheld the constitutional validity of the Scheduled Castes and
the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Amendment Act, 2018.
The amendment act
was challenged on the grounds of violation of the fundamental right to equality (Article 14) and personal
liberty (Article 21). The amendment act
adds article 18A which states that the preliminary enquiry shall not be
required for registration of a First Information Report against any person. It
also delineates specific crimes against Scheduled Castes and
Scheduled Tribes as atrocities and describes
strategies and prescribes punishments to counter
these acts.
National Crime Record Bureau
NCRB, headquartered in New Delhi, was set-up in 1986 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators. It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).NCRB brings out the annual comprehensive statistics of crime across the country (‘Crime in India’ report). Being published since 1953, the report serves as a crucial tool in understanding the law and order situation across the country.